I am learning how to install an Infor ION Grid laboratory from scratch without LifeCycle Manager (LCM). I had started in part 2 with a minimalist Grid. Today, I will add the Default Router, Developer Session Provider, Administrative Router, Configuration Manager, web user interface, and Grid Agent.
BUT WHY?

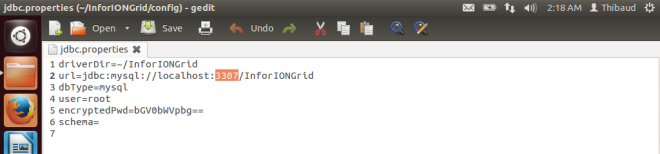
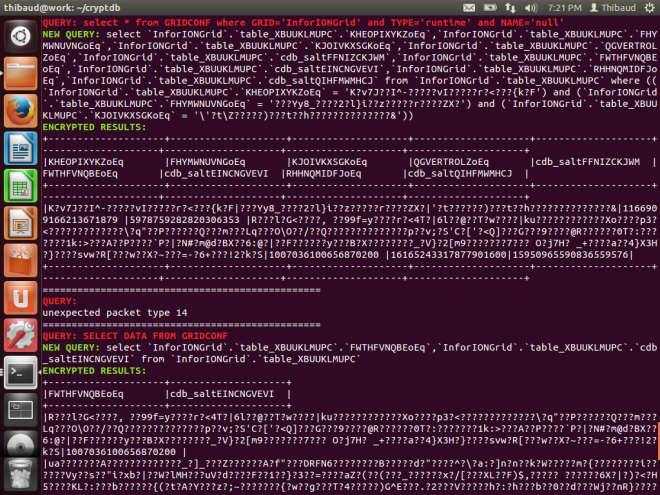
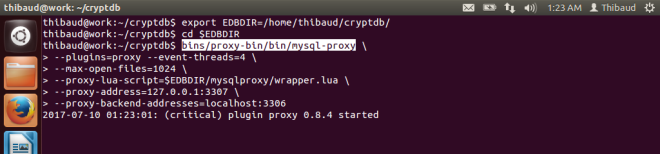
I am learning the guts of the Grid because I am curious by nature, because I want to do penetration testing, because I want to install M3 on Linux and PostgreSQL to promote free software (as in freedom), and I want to make a proof-of-concept of M3 (just the Grid for now) on a homomorphic encryption database such as CryptDB or Microsoft’s Always Encrypted SQL Server.
Learning process
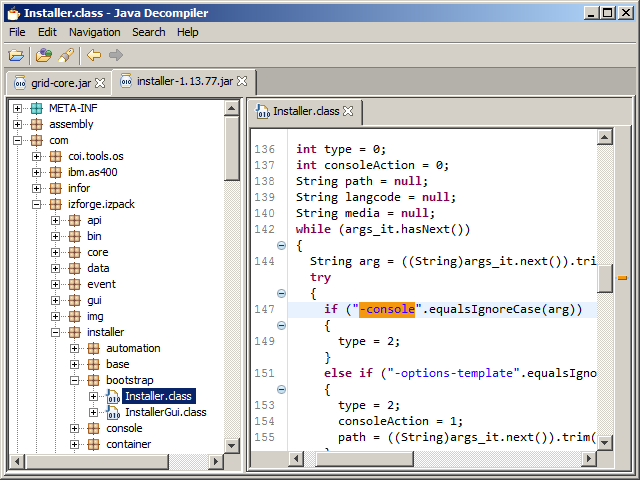
To learn, I take any installed Grid as a reference, and I study its internals. I start from the Topology View, I select the Node of interest (e.g. Administrative Router), I look at the Properties to make note of the command that launches it, I look at the Threads to determine the Java class name, I look at the disassembled source code to assimilate what it does, I look at the LCM installation package to understand the Velocity scripts and Ant tasks (see my previous work on LCM), and I look at the public Infor documentation. Then, I try to reproduce the Grid in my laboratory with only the necessary and sufficient elements. Here are some screenshots while learning the Grid Administrative Router:




I must use this Chinese wall technique because as a consultant I do not have access to Infor Product Development, i.e. the developers do not respond to my questions, and they do not share their source code or internal documentation. I am known for having “crazy ideas”, supposedly pointless. I call it progress 😉 If we do not challenge the status quo, who will? Even if I had access to the internal details, I am not allowed to show proprietary information. The workaround is to put myself in the situation of a clean room, analogous to that of any customer that has access to the binaries and that can reverse engineer on their own. That is how I can share my results here. Nonetheless, congratulations to Infor for finally having made a lot of the documentation public; please encourage them as well. In that direction, please sign the petition so Infor makes their source code at least source-available or shared source, and so they cooperate more with developers.

1. Begin with minimal Grid
Follow part 2 to begin with a minimal Grid.
2. Additional JAR files
Get the following additional JAR files (I may need to clean up the list). These JAR files are packed with IzPack at Grid_Installer_11.1.13.0.77.lcm\products\Infor_ION_Grid_11.1.13.0\components\installer-1.13.77.jar\resources\packs\ . More easily, I get them from my existing Grid installation of part 4. Then, put them somewhere, e.g. C:\Infor\Grid\resources\ :
resources\1.13.77\jna-3.3.0-platform.jar
resources\1.13.77\jna-3.3.0.jar
runtimes\1.13.77\jaxrs2Resources\grid-jaxrs2-1.13.77.jar
runtimes\1.13.77\jaxrs2Resources\hk2-api-2.2.0.jar
runtimes\1.13.77\jaxrs2Resources\hk2-locator-2.2.0.jar
runtimes\1.13.77\jaxrs2Resources\hk2-utils-2.2.0.jar
runtimes\1.13.77\jaxrs2Resources\jackson-core-asl-1.9.13.jar
runtimes\1.13.77\jaxrs2Resources\jackson-jaxrs-1.9.13.jar
runtimes\1.13.77\jaxrs2Resources\jackson-mapper-asl-1.9.13.jar
runtimes\1.13.77\jaxrs2Resources\javassist-3.18.1-GA.jar
runtimes\1.13.77\jaxrs2Resources\javax.annotation-api-1.2.jar
runtimes\1.13.77\jaxrs2Resources\javax.inject-2.2.0.jar
runtimes\1.13.77\jaxrs2Resources\javax.ws.rs-api-2.0.jar
runtimes\1.13.77\jaxrs2Resources\jersey-client-2.7.jar
runtimes\1.13.77\jaxrs2Resources\jersey-common-2.7.jar
runtimes\1.13.77\jaxrs2Resources\jersey-container-servlet-core-2.7.jar
runtimes\1.13.77\jaxrs2Resources\jersey-guava-2.7.jar
runtimes\1.13.77\jaxrs2Resources\jersey-media-json-jackson-2.7.jar
runtimes\1.13.77\jaxrs2Resources\jersey-media-multipart-2.7.jar
runtimes\1.13.77\jaxrs2Resources\jersey-server-2.7.jar
runtimes\1.13.77\jaxrs2Resources\mimepull-1.9.3.jar
runtimes\1.13.77\jaxrs2Resources\validation-api-1.1.0.Final.jar
runtimes\1.13.77\tools\grid-cli\jackson-core-asl-1.9.13.jar
runtimes\1.13.77\tools\grid-cli\jackson-mapper-asl-1.9.13.jar
runtimes\1.13.77\webAppResources\commons-fileupload-1.2.2.jar
runtimes\1.13.77\webAppResources\grid-webapp-1.13.77.jar
runtimes\1.13.77\webAppResources\javax.websocket-api-1.0.jar
runtimes\1.13.77\webAppResources\javax-websocket-client-impl-9.1.1.v20140108.jar
runtimes\1.13.77\webAppResources\javax-websocket-server-impl-9.1.1.v20140108.jar
runtimes\1.13.77\webAppResources\javax.annotation-api-1.2.jar
runtimes\1.13.77\webAppResources\jetty-http-9.1.1.v20140108.jar
runtimes\1.13.77\webAppResources\jetty-io-9.1.1.v20140108.jar
runtimes\1.13.77\webAppResources\jetty-security-9.1.1.v20140108.jar
runtimes\1.13.77\webAppResources\jetty-server-9.1.1.v20140108.jar
runtimes\1.13.77\webAppResources\jetty-servlet-9.1.1.v20140108.jar
runtimes\1.13.77\webAppResources\jetty-servlets-9.1.1.v20140108.jar
runtimes\1.13.77\webAppResources\jetty-util-9.1.1.v20140108.jar
runtimes\1.13.77\webAppResources\websocket-api-9.1.1.v20140108.jar
runtimes\1.13.77\webAppResources\websocket-client-9.1.1.v20140108.jar
runtimes\1.13.77\webAppResources\websocket-common-9.1.1.v20140108.jar
runtimes\1.13.77\webAppResources\websocket-server-9.1.1.v20140108.jar
runtimes\1.13.77\webAppResources\websocket-servlet-9.1.1.v20140108.jar

3. CLASSPATH
Prepare a CLASSPATH environment variable with all the JAR files including the JDBC driver:
set CLASSPATH=drivers\sqljdbc42.jar;resources\bcmail-jdk16.jar;resources\bcprov-jdk16.jar;resources\commons-fileupload-1.2.2.jar;resources\grid-core.jar;resources\grid-jaxrs2-1.13.77.jar;resources\grid-webapp-1.13.77.jar;resources\grid.httpclient.jar;resources\grid.liquibase.jar;resources\hk2-api-2.2.0.jar;resources\hk2-locator-2.2.0.jar;resources\hk2-utils-2.2.0.jar;resources\jackson-core-asl-1.9.13.jar;resources\jackson-jaxrs-1.9.13.jar;resources\jackson-mapper-asl-1.9.13.jar;resources\javassist-3.18.1-GA.jar;resources\javax-websocket-client-impl-9.1.1.v20140108.jar;resources\javax-websocket-server-impl-9.1.1.v20140108.jar;resources\javax.annotation-api-1.2.jar;resources\javax.inject-2.2.0.jar;resources\javax.servlet-api.jar;resources\javax.websocket-api-1.0.jar;resources\javax.ws.rs-api-2.0.jar;resources\jersey-client-2.7.jar;resources\jersey-common-2.7.jar;resources\jersey-container-servlet-core-2.7.jar;resources\jersey-guava-2.7.jar;resources\jersey-media-json-jackson-2.7.jar;resources\jersey-media-multipart-2.7.jar;resources\jersey-server-2.7.jar;resources\jetty-http-9.1.1.v20140108.jar;resources\jetty-io-9.1.1.v20140108.jar;resources\jetty-security-9.1.1.v20140108.jar;resources\jetty-server-9.1.1.v20140108.jar;resources\jetty-servlet-9.1.1.v20140108.jar;resources\jetty-servlets-9.1.1.v20140108.jar;resources\jetty-util-9.1.1.v20140108.jar;resources\jna-3.3.0-platform.jar;resources\jna-3.3.0.jar;resources\mimepull-1.9.3.jar;resources\validation-api-1.1.0.Final.jar;resources\websocket-api-9.1.1.v20140108.jar;resources\websocket-client-9.1.1.v20140108.jar;resources\websocket-common-9.1.1.v20140108.jar;resources\websocket-server-9.1.1.v20140108.jar;resources\websocket-servlet-9.1.1.v20140108.jar

4. Additional folders
Create the following additional folders, I leave them empty even though I could organize the JAR files accordingly:
jaxrs2Resources
webAppResources
webServiceResources
webStartResources

And create file webStartResources\webStartResources.properties, even though empty.
5. Additional tables
Create the following additional database tables:
CREATE TABLE KEY_VALUE_STORE (
APPLICATION_NAME varchar(64) NOT NULL,
PROPERTY_NAME varchar(256) NOT NULL,
PROPERTY_KEY varchar(128) NOT NULL,
PROPERTY_VALUE varbinary(max) NULL,
PROPERTY_TYPE varchar(256) NOT NULL,
PROPERTY_SIZE numeric(10, 0) NOT NULL,
SEQID numeric(5, 0) NOT NULL,
TIMESTAMP numeric(20, 0) NOT NULL,
)
CREATE TABLE HOSTS(
GRID_NAME varchar(64) NOT NULL,
HOST_NAME varchar(64) NOT NULL,
VALID_CERT varchar(32) NOT NULL,
MODIFIED_BY varchar(128) NULL,
DEPLOY_STATE varchar(32) NOT NULL,
TIMESTAMP numeric(20, 0) NOT NULL,
RUNNING varchar(32) NOT NULL,
GRID_VERSION varchar(64) NOT NULL,
BOOTSTRAP_VERSION varchar(64) NULL,
HTTP_PORT numeric(20, 0) NOT NULL
)
INSERT INTO HOSTS (GRID_NAME, HOST_NAME, VALID_CERT, MODIFIED_BY, DEPLOY_STATE, TIMESTAMP, RUNNING, GRID_VERSION, BOOTSTRAP_VERSION, HTTP_PORT) VALUES ('Grid', 'localhost', 'true', 'Thibaud', 'ACTIVE', 0, 'STARTED', '1.13.77', '1.13.77', 50002)
6. Default Router
The Default Router is what Grid clients will connect to by default to communicate with the Grid.
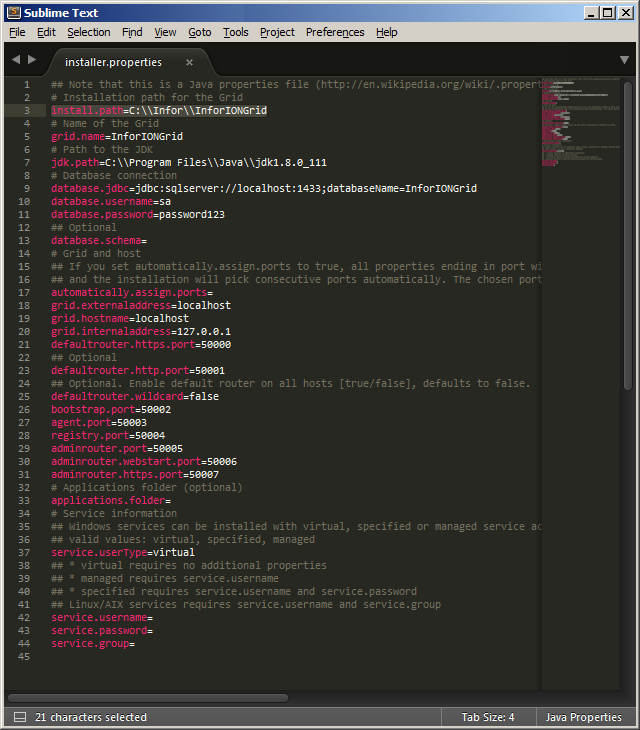
Add the following to <routers> in the runtime.xml in the GRIDCONF table:
<router name="Default Router" host="localhost" httpsPort="50000" httpPort="50001" />
Use this command to start the Default Router:
java -cp %CLASSPATH% com.lawson.grid.Startup -router "Default Router" -configDir C:\Infor\Grid\ -host localhost -logLevel ALL
7. Developer Session Provider
The Developer Session Provider will let us login with any user and password (e.g. grid-admin) and get a session.
Add the following to <runtime> in the runtime.xml in the GRIDCONF table:
<sessionProviders developer="true" />


8. Administrative Router
The administrative router is the server part of the Configuration Manager.
Add the following to <topology> in the topology.xml in the GRIDCONF table:
<administrativeRouter host="localhost" port="50005" webStartPort="50006" httpsPort="50007" />
Use this command to start the Administrative Router:
java -cp %CLASSPATH% com.lawson.grid.Startup -router "Administrative Router" -configDir C:\Infor\Grid\ -host localhost -logLevel ALL
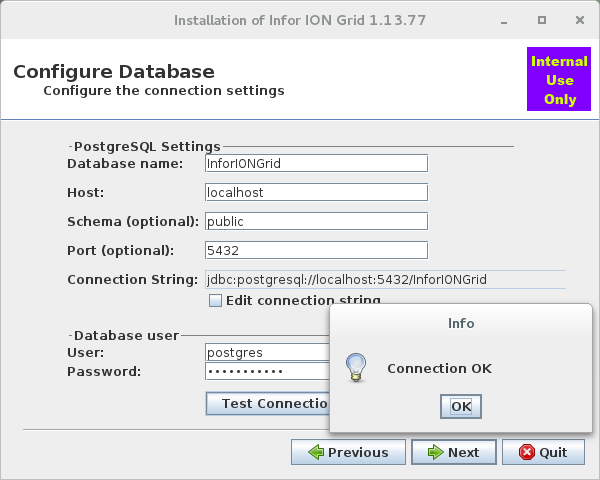
9. Configuration Manager Client
The Configuration Manager Client is the user interface to manage the runtime.xml.
You can use the online client from the Grid Management Pages:

Or you can use this command to start the offline client:
java -cp %CLASSPATH% com.lawson.grid.config.client.ui.Launch


10. Web UI
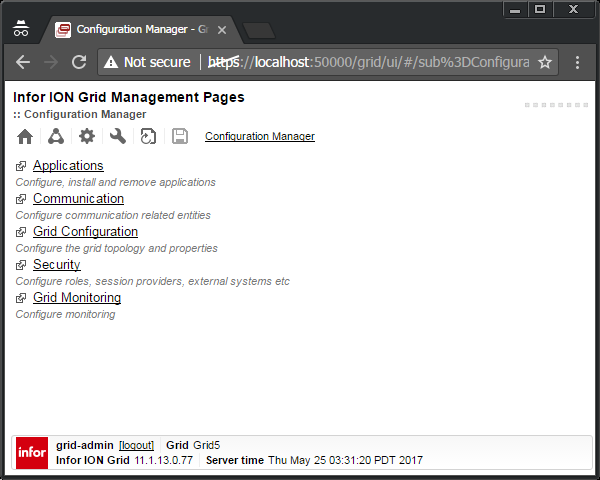
Start the Grid web user interface by opening a browser to https://localhost:50000/grid/info.html , then select /grid/ui/ , then go to the Configuration Manager and login:

11. Start the Grid
To start the Grid:
- Start the Registry as shown previously in part 2:
-
java -cp %CLASSPATH% com.lawson.grid.Startup -registry -configDir C:\Infor\Grid\ -host localhost -logLevel ALL
- Start the Default Router as shown above.
- Start the Administrative Router as shown above.
Now we can start the Configuration Manager Client and/or web UI as shown above and enjoy the Grid.
Result
We now have a minimal Grid with the Configuration Manager and fewer error messages:

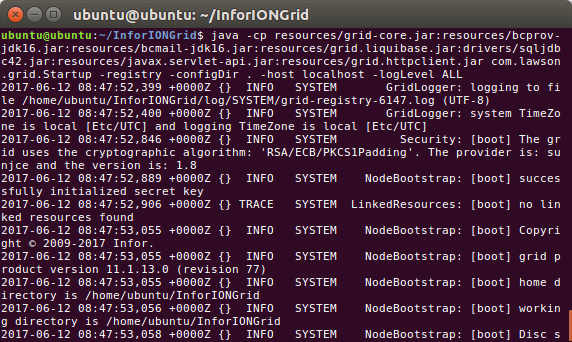
Optional – Grid Agent
Instead of starting the Grid manually piece by piece, we can let the Grid Agent start it all. The Grid Agent is used to start nodes programmatically (e.g. registry, routers, applications); there is one Grid Agent per host. The Windows Service Infor ION Grid Bootstrap uses the Grid Launcher and Grid Agent to launch everything in the Grid at startup: registry, routers, applications, etc.:
java -cp %CLASSPATH% com.lawson.grid.agent.GridAgent -configDir C:\Infor\Grid\ -logToConsole -logLevel ALL -host localhost


Note: The Grid Agent will attempt to create the database tables, but because we already have some tables, not all of them, it will stop. Delete all the tables from the Grid database; re-run the Grid Agent, it will create all the tables; re-import the GRIDCONF with runtime.xml and topology.xml; re-run the Grid Agent.
Note: To stop the Grid, if we simply close the Grid Agent command prompt to terminate the batch job, it will not terminate the Java processes. We must go in the Task Manager and end the three java.exe processes for the registry, default router, and administrative router:

GitHub
I put the SQL and commands on my GitHub.
Future work
I hope to do the following soon:
- Install Grid session providers
- Install GDBC
- Install Grid applications
- Install the Grid on Linux and PostgreSQL
- Penetration testing
- Proof-of-concept of Grid database on homomorphic encryption with CryptDB or Microsoft’s Always Encrypted SQL Server
Conclusion
That was a continuation of part 2 of building an Infor Grid laboratory for learning purposes, beginning with a minimal Grid, and adding a Default Router, Developer Session Provider, Administrative Router, Configuration Manager, web user interface, and Grid Agent. I can probably polish some of it. I will continue in the next posts.
That’s it!
Please like, comment, subscribe, share, and come write the next idea.
Related posts